
By Vani van Nielen, Larina Maira Laube, Eliana Levine, Zhaoyu Zhu, Paloma Guerra and Alex Sogno.
Three weeks ago, Marriott International announced it had experienced a data breach, putting the personal data of 5.2 million guests at risk. While this number dwarfs in comparison to the data breach of 500 million Marriott and Starwood guests in late 2018, the message is clear – hotels are a target for threats and need to focus on protecting their employees’ and guests’ data. With the advent of COVID-19, your company’s cyber security is at higher risk. As employees worldwide switch to working from home, the dangers associated with mobile devices, remote access to core business systems, and poor online practices are increasing. Meanwhile, as seen below, hackers have been heightening their malicious efforts knowing that businesses are more vulnerable now.
Figure 1 – Percentage of Traffic Blocked on Travel and Hospitality Sites from February 2nd – March 22nd, 2020.
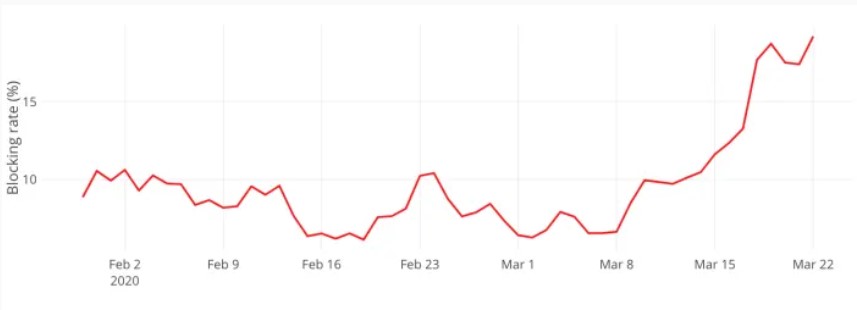
While managers these days are, understandably, focusing mostly on staying financially afloat, it is important to keep cyber security a priority. Hacks resulting from stolen or lost employee login credentials can have tremendous impacts, whether you’re a small independent hotel or an international hotel giant. Following the ISO 22301 Business Continuity Standards, cyber security is crucial to your enterprise’s resilience. It is your responsibility as an employer to give your employees the tools to protect themselves, which will end up protecting your guests, reputation, and bottom line.
We’ve organised key risk treatment and mitigation measures into the following guidelines:
1. Multi-Factor Authorisation
Two (2FA) or multi-factor authorisation is one of the most effective ways to prevent Account Takeovers (ATOs). Essentially, this consists of using one or more authorisation methods in addition to a password to log in to your account. SMSs are safer than emails as a second factor, as it is more difficult to access a phone’s details than an email password. According to an article by Hospitality Technology, it is highly likely a recent breach at a large hotel brand company was caused by a phishing attack that stole the credentials of two employees. ATOs have shown a steep rise following the virus. According to the Director of Identity Security at Microsoft, your account is more than 99.9% less likely to be compromised if you use MFA.
2. Update, Update, Update
As potential security breaches are found, reported, and fixed by the affected platforms, new updates are consistently rolled out. Strengthening your cyber security is as simple as constantly checking and updating various applications. Actively encourage your team to update all applications they use. If there is an update in a crucial platform used in your business, such as a file-sharing platform, video conference application, or VPN, try to email employees a reminder to update.

3. Beware of Scams
Scammers are taking advantage of fears surrounding the Coronavirus by sending emails with viruses, scams, and misinformation. Inform your employees to be alert and wary with emails regarding COVID-19 asking them to open a link or download a program, even if they seem to be from their colleagues or respected authorities like the WHO. Ask your employees to share suspicious emails with the rest of the team so that everyone can be on the lookout for them.
4. Virtual Private Networks (VPN)
While your business will likely already be using a VPN for employees to access business servers, it is a crucial step for cyber security. VPNs ensure a higher level of security and safety between the remote worker and the business server. Ensure you set up multi-factor authorisation for employees to access the VPN and update whenever possible. Ensure your VPN usage policy is clear, so your team knows what applications they shouldn’t use with it on.
5. Company Approved Devices and Private WiFi Networks
If your employees do not work on company-issued devices, ensure you are clear with what devices they can and cannot use for work. For example, using mobile devices should be strongly discouraged for work purposes, as they are likely to automatically connect to public WiFi networks should they leave the house. Public WiFi networks open up your employees and company data to threats, especially when used to access your VPN. Make sure your employees only use private WiFi and consider supplying them with reliable anti-virus software and firewalls if they do not have them already.

6. Video Conferencing Measures
While these tips are tailored for Zoom users, similar measures are also possible on alternatives such as GoToMeeting, Cisco Webex etc. Other than constantly updating, try to change your Personal Meeting ID (PMI), as infiltrators compile lists of known PMIs. Ensure you set passwords for important meetings, and send the passwords separately from the PMI as close to the meeting time as you can. Take advantage of Zoom’s waiting room feature, which prevents people from joining the call before the host, and allows you to keep tabs on who wants to join. Once the session has started with the essential participants, lock the meeting to prevent infiltrators from joining once everyone is distracted.
Finally, change the call settings to allow only one application to be used when sharing the screen. This prevents the chances of employees accidentally showing sensitive information open on other windows when sharing their screen.
7. Cloud File Storage
File sharing and storage tools on a cloud platform give your team agile access to documents in a teleworking environment. If your company server has decided on a file-sharing platform, such as OneDrive, remind employees that they should not use other servers like Google Drive for corporate files. We recommend you assign specific people the responsibility of supervising the permissions assigned to folders and documents that are stored on these platforms, ensuring that only those people with correct credentials have access. Sensitive or regulated records (personal data, financial information, etc.) should be encrypted using Information Rights Management (IRM) technologies. Then, even once documents are downloaded from the cloud, the data is still protected and controlled. IRM can even revoke access once the documents no longer need to be available.

8. Clear Usage Policies and Employee Support
The guidelines above will not be useful unless adequately communicated to your team. Decide which platforms should be used for every business function (VPN, file sharing, video conferencing, etc) and inform everyone that only these can be used for work purposes.
Be understanding to your employees, as many might be struggling to quickly learn new technologies and remote working guidelines amidst the already stressful situation. Where possible, share tips and how-to’s for your employees who are new to specific technologies, and share this list of best practices. Make it clear who your team should inform if they suspect that their data has been breached. Foster a positive environment encouraging members to speak up about these suspicions, even if they feel they are at fault. This is the only way to mitigate the potential risks from spreading company-wide and ultimately affecting your bottom line.
This article was provided by Global Asset Solutions and republished with permission. To read the source version, including source references, please CLICK HERE.

